Breathing for the Sake of Science
Description
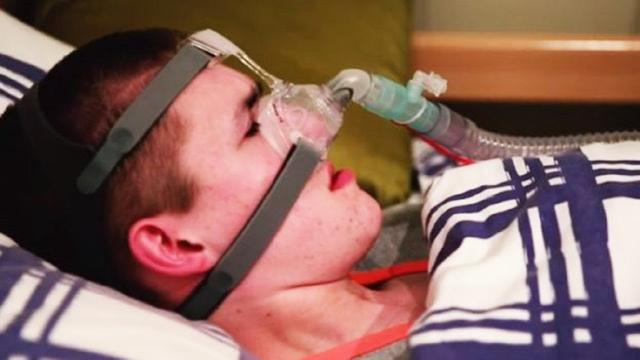
For five years, researchers with the European Space Agency have analyzed exhaled Nitric Oxide in astronauts’ breath to detect dust and other toxins. Future astronauts on the Moon or Mars could inhale
dust that has collected in their habitats or on their spacesuits potentially inflaming their airways.
Monitoring a crewmember’s airways could improve the mission environment and optimize crew health for a successful long-term mission. The research has also contributed to asthma diagnosis and treatment back on Earth. This week the crew completed the final session on the final subject for the investigation.
More: https://go.nasa.gov/2WRPVeZ
Follow updates on the science conducted aboard the space station on Twitter:
https://twitter.com/iss_research
For more information on how you can conduct your research in microgravity, visit https://go.nasa.gov/2q84LJj.